Why Does The Government Set Price Floors

When government laws regulate prices instead of letting market forces determine prices it is known as price control.
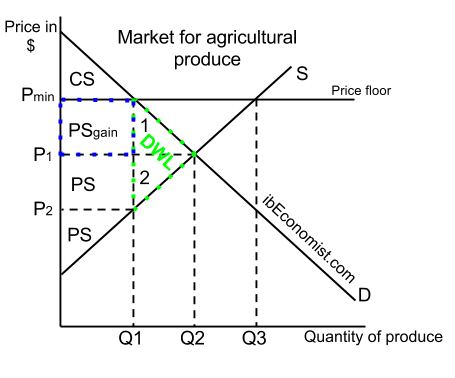
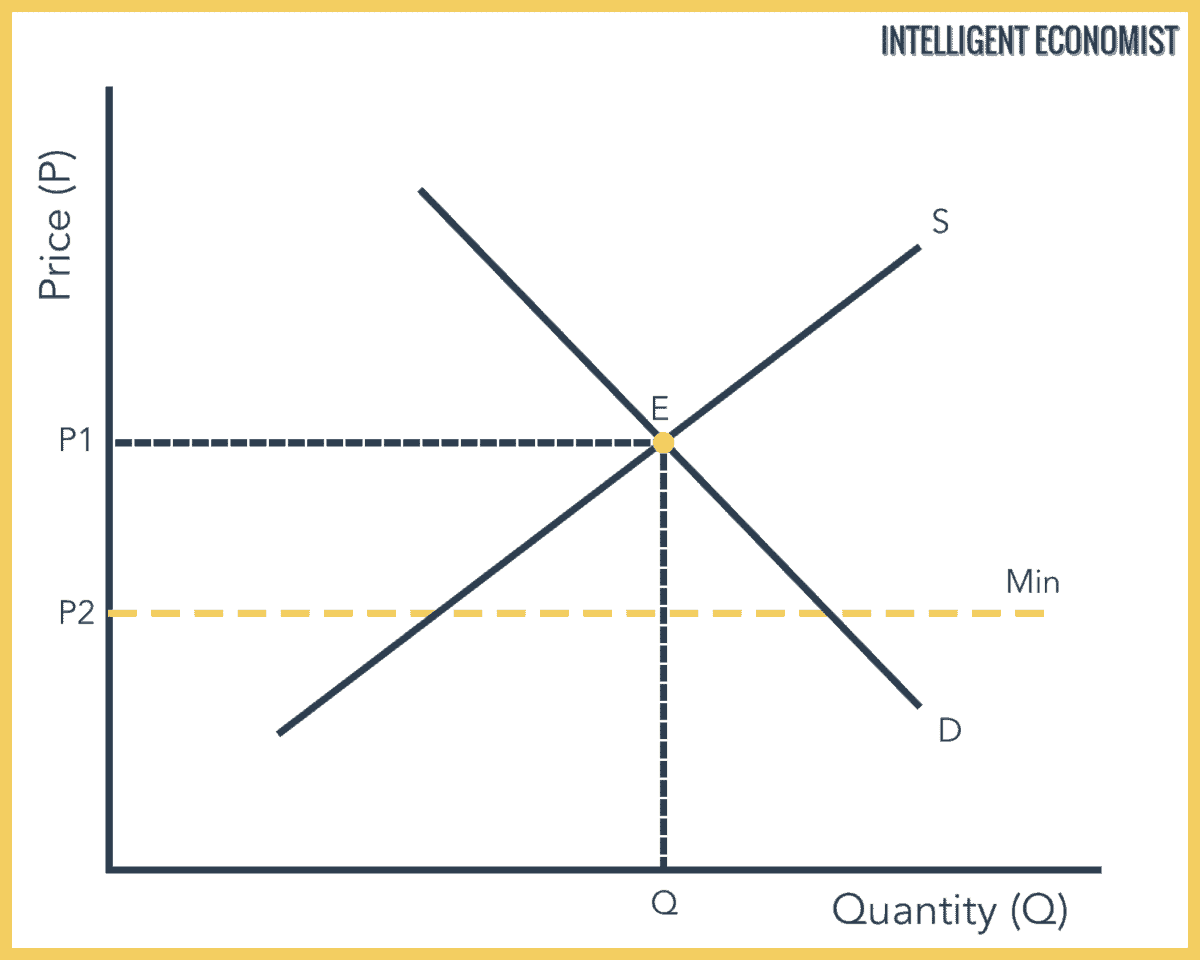
Why does the government set price floors. It is argued farmers incomes are too low. For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price. In order for a price ceiling to be effective it must be set below the natural market equilibrium. A minimum price is when the government don t allow prices to go below a certain level.
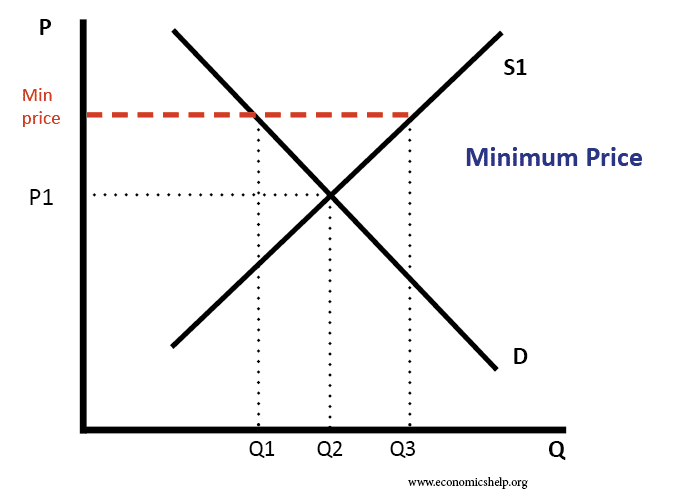
Governments often seek to assist farmers by setting price floors in agricultural markets. A minimum allowable price set above the equilibrium price is a price floor a minimum allowable price set above the equilibrium price. When a price ceiling is set a shortage occurs. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor. Price ceilings a price ceiling occurs when the government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be. Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. With a price floor the government forbids a price below the minimum.
Governments often seek to assist farmers by setting price floors in agricultural markets. Types of price floors 1. With a price floor the government forbids a price below the minimum. A minimum allowable price set above the equilibrium price is a price floor.
A local government for example might set a price floor on parking fees in a. Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low. Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers. Price floors and price ceilings are government imposed minimums and maximums on the price of certain goods or services.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. This is usually done to protect buyers and suppliers or manage scarce resources during difficult economic times.
For example the eu has used minimum prices for agriculture.